A) decreases osteoblast activity.
B) decreases osteocyte activity.
C) decreases osteochondral progenitor cell activity.
D) is associated with decreased osteoclast activity.
E) has no effect on bone cells.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most common bone disease is osteoporosis. The most common consequence of this disease is
A) fractures.
B) bone thickening.
C) luxations and subluxations.
D) fusion of bones.
E) remodeling of bone.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Osteogenesis imperfecta can be caused by abnormally formed
A) proteoglycans.
B) hydroxyapatite.
C) calcium.
D) collagen.
E) osteoblasts.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
These are blood vessels that carry blood from the medullary cavity and periosteum to the osteon and run perpendicular to the long axis of the bone.
A) Haversian canals
B) Volkmann canals
C) lamellar canals
D) osteochondral canals
E) Sharpey's canals
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bone fracture generally found in children that is incomplete is a(an)
A) complicated fracture.
B) hairline fracture.
C) spiral fracture.
D) dentate fracture.
E) greenstick fracture.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
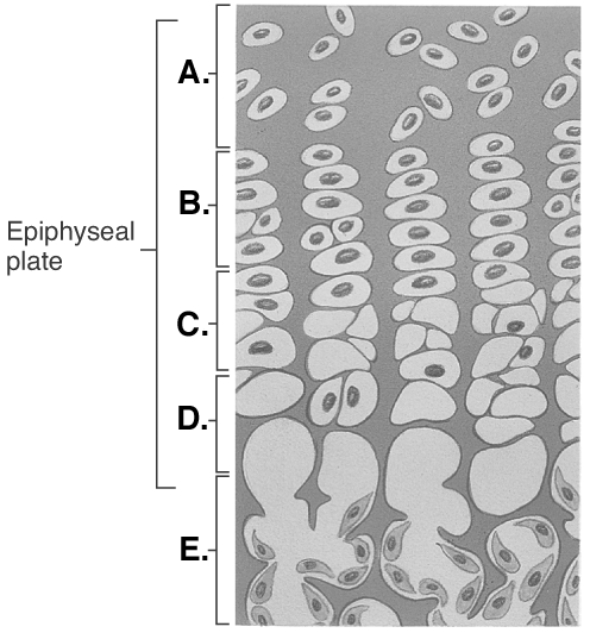 -This figure illustrates bone growth in length at the Epiphyseal Plate. What is zone "B"?
-This figure illustrates bone growth in length at the Epiphyseal Plate. What is zone "B"?
A) bone of diaphysis
B) zone of calcification
C) zone of hypertrophy
D) zone of proliferation
E) zone of resting cartilage
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The flat bones of the skull develop from
A) hyaline cartilage.
B) areolar tissue.
C) compact bone.
D) fibrous connective tissue.
E) fibrocartilage.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A connective tissue sheath around cartilage is the
A) endosteum.
B) perichondrium.
C) periosteum.
D) epiphyseal line.
E) ligament.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A) short bone - carpal bone
B) long bone - vertebra
C) irregular bone - femur
D) flat bone - phalanges of the toes
E) short bone - humerus
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rickets is
A) bone inflammation that often results from bacterial infection.
B) a disease in adults, especially women, characterized by a reduced amount of bone matrix.
C) a disease in adults characterized by softening of bones resulting from calcium depletion.
D) a disease in children characterized by soft, bowed, and swollen bones.
E) a group of genetic disorders producing very brittle bones that are easily fractured; occurs because of insufficient collagen development.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cartilage
A) is composed of osteons.
B) is surrounded by a membrane called the periosteum.
C) contains chondrocytes located in lacunae.
D) does not need nutrients and oxygen so it has no blood vessels.
E) is well vascularized.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The locations where ossification begins in intramembranous ossification are known as
A) secondary ossification centers.
B) membranous ossification centers.
C) centers of ossification.
D) medullary cavity ossification centers.
E) epiphyseal ossification centers.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The connective tissue sheath of cartilage is called the
A) matrix.
B) chondrocyte.
C) ligamentous cord.
D) lacuna.
E) perichondrium.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spongy bone tissue
A) is very dense.
B) contains concentric lamellae.
C) contains interconnecting plates called trabeculae.
D) has many spaces and lacks osteocytes.
E) is the primary component of compact bone.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A passageway connecting neighboring osteocytes in an osteon is a
A) central canal.
B) lamella.
C) canaliculus.
D) lacuna.
E) osteocanal.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bone fracture in which the two bone sections do not separate is a(an)
A) open fracture.
B) closed fracture.
C) comminuted fracture.
D) impaction fracture.
E) hairline fracture.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
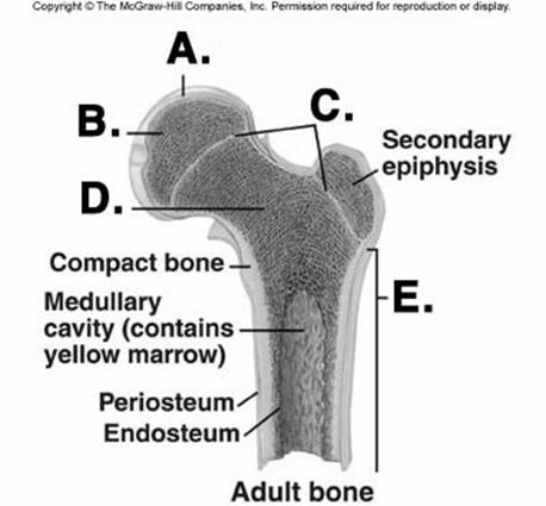 -What does structure "E" represent on the bone diagram?
-What does structure "E" represent on the bone diagram?
A) cancellous bone
B) diaphysis
C) epiphyseal lines
D) articular cartilage
E) epiphysis
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of bone cells have processes that lie in canaliculi?
A) osteochondral progenitor cell
B) osteoblasts
C) osteocytes
D) osteoclasts
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The proportion of collagen to hydroxyapatite in bone determines the
A) thickness of the bone.
B) length of the bone.
C) strength of the bone.
D) ability of the bone to heal.
E) growth rate of bone.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
These collagen fibers help to connect ligaments and tendons to the periosteum of the bone.
A) endosteal fibers
B) Sharpey fibers
C) Golgi fibers
D) Haversian fibers
E) Purkinje fibers
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 150
Related Exams