A) The concentration of hydroxide decreases to neutralize the excess hydronium.
B) The concentration of OH- stays the same but the ratio OH-/H3O+ changes.
C) The concentration of OH- increases but the ratio stays the same.
D) The concentration of OH- increases.
E) none of the above
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The main component of bleach is sodium hypochlorite, NaOCl, which consists of sodium ions, Na⁺, and hypochlorite ions, 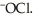 What products are formed when this compound is reacted with the hydrochloric acid, HCl, of toilet bowl cleaner?
What products are formed when this compound is reacted with the hydrochloric acid, HCl, of toilet bowl cleaner?
A) The products are NaCl, ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
B) The products are NaOH, ![]() O, and
O, and ![]()
C) The products are NaCl and HOCl.
D) The products are NaOH, ![]() , and
, and ![]()
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the pH of a solution was 7 and you were to increase the hydronium ion concentration 1000x, what would the pH be?
A) 4
B) 4 M
C) 1 × 10-4 M
D) 7,000 M
E) 10
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the source of acid rain?
A) Acid rain is from dissolved carbon dioxide.
B) All rain is acid rain because rain has a pH is less than 7.
C) Rain is normally basic, but depending on the weather it can get slightly acidic.
D) All rain is acid rain because rain has a hydronium ion concentration greater than 10-7 M.
E) none of the above
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following items would you use to make an acidic buffer solution?
A) acetic acid (a weak acid) and hydrochloric acid (a strong acid)
B) hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) and sodium chloride
C) acetic acid (a weak acid) and sodium acetate
D) hydrochloric acid (a strong acid) and sodium hydroxide (a strong base)
E) ammonium hydroxide (a weak base) and ammonium chloride
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the pH of a solution is 10, what is the hydroxide ion concentration?
A) 1 × 10-4 M
B) 4 M
C) 14 M
D) -14 M
E) - 1 × 1014 M
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you had a 1 M solution of a weak acid what would be its pH?
A) 1
B) 6
C) 7
D) 8
E) 13
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How readily an acid donates a hydrogen ion is a function of how well the acid is able to accommodate the resulting negative charge it gains after donating. Which should be the stronger acid: water or hypochlorous acid? Why? 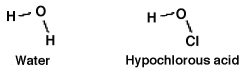
A) Water, because O-H would accommodate the resulting negative charge better than O-Cl.
B) Hypochlorous acid, because the resulting negative charge is spread over a greater number of atoms.
C) Neither, since both molecules are "monoprotic" and donate the same H+ ion, making their the same.
D) Water, because the hydrogen bonding in water gives it the edge in the ability to accommodate the resulting negative charge.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following reaction, identify whether the compound in bold is behaving as an acid or a base. H3PO4 + H2O ⇌ H2PO4- + H3O+
A) acid
B) base
C) neither
D) both
E) none of the above
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Does the hydride ion, H⁻, tend to behave as an acid or a base?
A) Hydride ion is unstable and re-reacts with water to form an acid in the form of the hydronium ion, H3O⁺.
B) Hydride ion has a pair of electrons and acts like a Lewis base since it has a strong tendency to lend or donate that electron pair.
C) Although the hydride ion has two electrons, they do not pair together. Thus, the hydride ion is incapable of acting as a Lewis base and therefore tends to behave as an acid.
D) Hydride ion's makeup consists of one proton and two electrons. As such, its tendency is to form neutral hydrogen gas, ![]() , and therefore is neither acidic nor basic, but neutral.
, and therefore is neither acidic nor basic, but neutral.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about strong and weak acids is not true?
A) A weak acid is not as corrosive as a strong acid.
B) A weak acid does dissociate in water.
C) A strong acid will react with a strong base.
D) A weak acid will react with a strong base.
E) All of the above are untrue.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following acid-base reaction, identify what compound is formed in the space marked. HNO3 + KOH ⇌ ???? + H2O
A) KNO3
B) H3ONO3
C) KOH2
D) KOH2NO3
E) none of the above
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why might an area with a large amount of limestone (CaCO3) be less susceptible to acid rain?
A) The acid in the rain is neutralized by the natural base in the limestone.
B) The rain travels quickly through the porous limestone and therefore the rate of reaction is slower.
C) Limestone is degraded by acid rain and therefore acid rain has the same damaging effects.
D) Only acid rain made from sulfur compounds reacts with the limestone.
E) none of the above
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following reactions illustrates an amphoteric compound?
A) 2 HF ⇌ H2F+ + F-
B) NaOH + HBr ⇌ NaBr + H2O
C) 2 H2 + O2 ⇌ 2 H2O
D) All are amphoteric.
E) none of the above
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which should be a stronger base: ammonia, 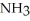 , or trifluoronitrogen,
, or trifluoronitrogen, 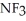 ? Why?
? Why? 
A) ![]() ; The fluorine atoms, being already highly electronegative, repel and tend to release the lone electron pair more easily, making it the stronger base.
; The fluorine atoms, being already highly electronegative, repel and tend to release the lone electron pair more easily, making it the stronger base.
B) ![]() ; The fluorines have greater electronegativities and pull the lone pair electrons closer to nitrogen, thus making
; The fluorines have greater electronegativities and pull the lone pair electrons closer to nitrogen, thus making ![]() less willing to release the electron pair and thus be a weaker base.
less willing to release the electron pair and thus be a weaker base.
C) ![]() ; Ammonia tends to form a very pungent but weak base.
; Ammonia tends to form a very pungent but weak base. ![]() will definitely form a stronger base since the highly polar fluorines have replaced the weak hydrogens.
will definitely form a stronger base since the highly polar fluorines have replaced the weak hydrogens.
D) Neither; The nitrogens are large enough to shield the effect of either the hydrogens or fluorines from exerting any appreciable influence over the electron pair. Both molecules will have nearly identical base strength.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a hydronium ion concentration equals 1 × 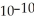 moles per liter, what is the pH of the solution? Is the solution acidic or basic?
moles per liter, what is the pH of the solution? Is the solution acidic or basic?
A) The pH of this solution is 4, which is acidic.
B) The pH of this solution is 8, which is basic.
C) The pH of this solution is 6, which is acidic.
D) The pH of this solution is 10, which is basic.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An acid and a base react to form a salt, which consists of positive and negative ions. Which forms the positive ions: the acid or the base? Which forms the negative ions?
A) The acid forms the positive ion, the base forms the negative ion.
B) The acid forms the negative ion, the base forms the positive ion.
C) Because different substances can act as an acid or a base, it depends on the substance you begin with.
D) all of the above
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As the pH increases, the hydroxide ion concentration ________.
A) goes down
B) gets larger
C) starts to affect the H+ concentration
D) starts to decrease because it is reacting with the excess hydronium ions
E) stays constant
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What happens to the pH of a 1M solution of hydrochloric acid, HCl, as carbon dioxide gas is bubbled into it?
A) The pH decreases as the solution becomes more acidic since carbon dioxide reacts to form carbonic acid thus increasing the overall acid concentration.
B) The pH increases as the solution becomes more basic since the carbon dioxide continues to tie up more and more of the hydrogen ions as associated carbonic acid molecules.
C) The pH remains unchanged. Carbon dioxide is unable to affect the pH in the presence of such a concentrated solution of such a strong acid.
D) At first the pH will increase as carbon dioxide ties up the hydrogen ions from the solution. Once the concentration of the resulting carbonic acid becomes greater than 1M, the pH will begin to decrease indicating the presence of more acid.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The overall rate at which humans are producing carbon dioxide is ________.
A) increasing
B) decreasing
C) some years increasing and other years decreasing
D) remaining about the same
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 135
Related Exams