A) a decrease in reaction rate.
B) an increase in the probability factor.
C) a decrease in the probability factor.
D) an increase in the reaction rate.
E) no changes.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Increasing the temperature of a reaction will speed up the overall rate as this will increase the energy of activation for reaction.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not true concerning the strength of a nucleophile?
A) Nucleophilicity may not parallel basicity.
B) Negatively charged nucleophiles are always more reactive than their conjugate acids.
C) The greater the strength of a nucleophile,the faster an SN2 reaction will occur.
D) Strong bases are always good nucleophiles
E) None of these answer choices are correct.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reaction, 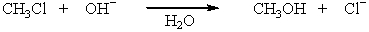 has the following thermodynamic values at 27.0 ºC: H = -75.3 kJ mol-1; S = 54.4 J K-1 mol-1.What is the value of G for this reaction?
has the following thermodynamic values at 27.0 ºC: H = -75.3 kJ mol-1; S = 54.4 J K-1 mol-1.What is the value of G for this reaction?
A) -73.8 kJ mol-1
B) -76.8 kJ mol-1
C) -59.0 kJ mol-1
D) +91.6 kJ mol-1
E) -91.6 kJ mol-1
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing the temperature of a chemical reaction usually increases greatly the rate of the reaction.The most important reason for this is that increasing the temperature
A) increases the collision frequency.
B) decreases the probability factor.
C) increases the fraction of collisions with energy greater than Eact.
D) decreases the energy of activation.
E) makes the reaction more exothermic.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the potential energy diagram that represents a two-step endothermic (endergonic) reaction. 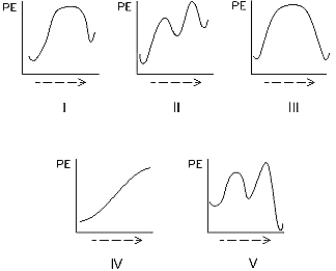
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in the bond energies of reactants and the transition state of a reaction is designated by the notation:
A) " H "
B) " H‡"
C) " G "
D) " G‡"
E) " S‡"
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A true statement about the transition state(s) of an SN2 reaction is:
A) The two transition states are of unequal energy.
B) The transition states precede and follow an unstable reaction intermediate.
C) The single transition state represents the point of maximum free energy of the reaction.
D) Existence of this transition state implies an exothermic reaction.
E) The transition state will always have a net charge of -1.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In a highly exergonic SN2 reaction we can assume the transition state is similar to the products formed in the reaction.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following alkyl bromide isomers would most readily undergo an SN2 reaction?
A) bromocyclobutane
B) 4-bromo-1-butene
C) 3-bromo-1-butene
D) 1-bromo-1-butene
E) All will react at the same rate.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is the weakest nucleophile in polar aprotic solvents?
A) I-
B) Br-
C) Cl-
D) F-
E) All of these choices are equally strong nucleophiles,regardless of the type of solvent used.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 91 of 91
Related Exams